Contact Us

Site Testing
We can undertake a range of site-based testing:
- In situ CBR and plate load testing
- DCP: Dynamic cone penetrometer (commonly referred to as the TRL probe)
- DP: Dynamic probing
- Soakaways and permeability testing
- Pressuremeter
All investigation techniques are undertaken in accordance with the corresponding British Standard and industry best practice.
Plate Load Testing
Plate load tests are used to directly assess the ultimate bearing capacity of the soil. They also provide an indication of the likely settlement under a given load. Various size plates can be used and should be selected based on the anticipated foundation size. However, larger plates require a larger reaction weight. We usually undertake these tests on sites with machines already there for us to borrow temporarily.
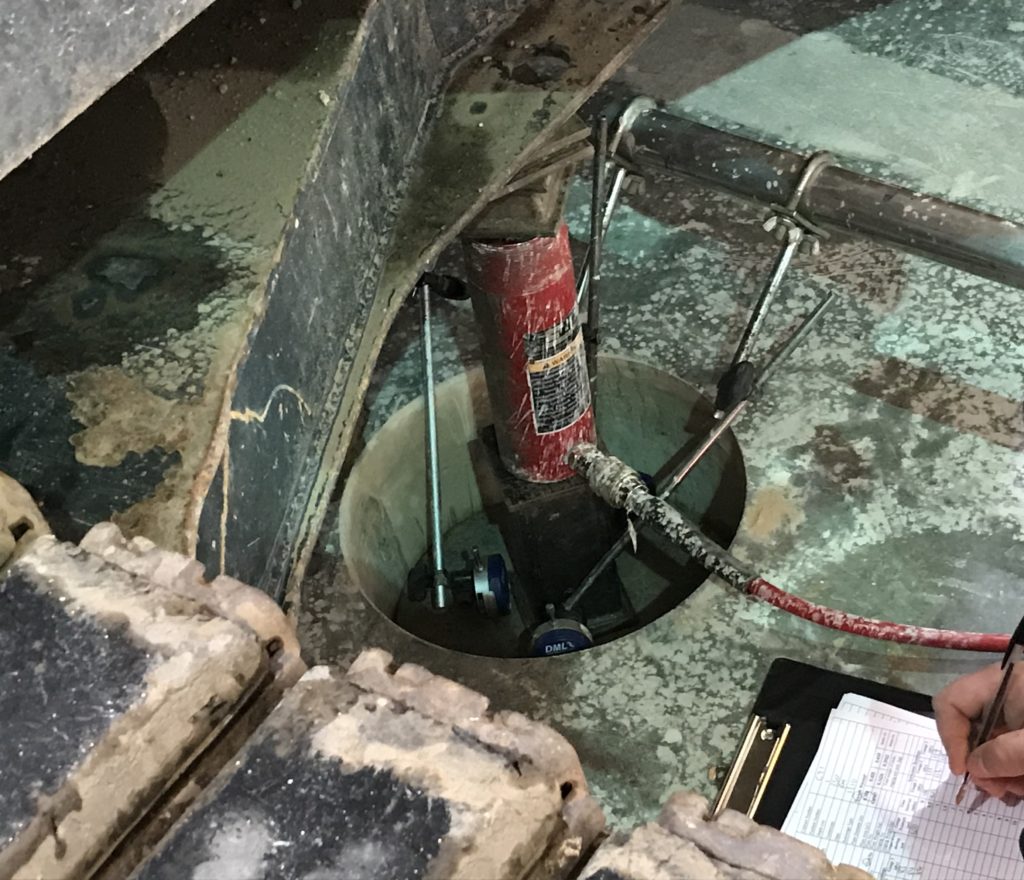
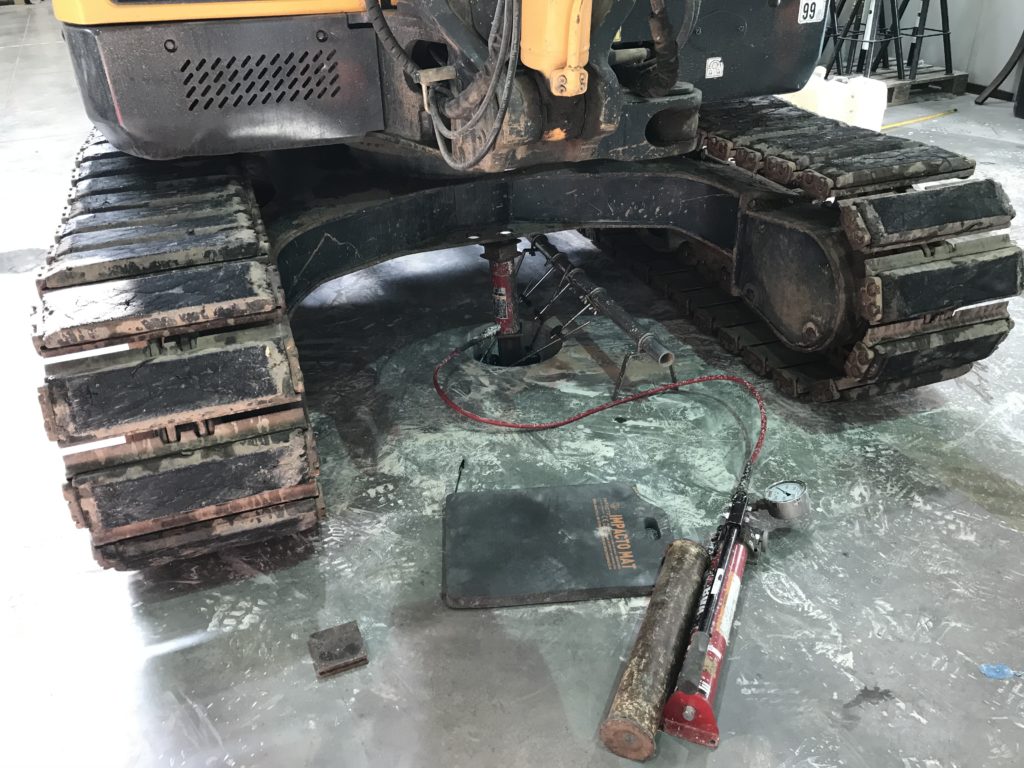


CBR Testing
Soil CBR values are widely used in the design of roads, car parks and similar applications. The CBR value directly influences the thickness of capping and subbase required for the scheme. It is therefore wise to accurately determine the site conditions so that the design is appropriate and not overly conservative.
The CBR (California Bearing Ratio) value of the soil is determined in various ways depending on the stage the project is at and if any cut and fill operations are planned.
In situ CBR Test
This test is normally undertaken at the time of main construction to validate design assumptions. The formation level is exposed and scraped level. A plunger is then advanced into the soil at a constant penetration rate. A reaction weight (kentledge) is required and usually provided in the form of an excavator or 4×4 vehicle. The applied stress is measured and used to determine the CBR. We can typically undertake 6-8 tests per shift.
Dynamic Cone Penetrometer (DCP)
These tests are usually undertaken as part of a site investigation prior to construction. The test is hand held and therefore access is rarely an issue. The test is undertaken in accordance with CS 229 (part of the DMRB) and involves using a drop hammer to drive a steel cone into the ground. We then interpret the results to determine the CBR within the soil. We can typically undertake 6-8 tests per shift.
Dynamic probing
Dynamic probing is a quick, cost-effective method of determining the relative resistance of the ground. It involves driving a steel cone vertically into the ground and measuring the number of blows to advance 100mm. The technique is best suited where a notable change in soil density is anticipated, for example, dissolution features or landfill extents.
Soakaway and permeability testing
Soakaways temporarily store surface water runoff before discharging to the ground, ready for the next storm event. Shallow soakaways are adopted where the near surface soils are likely to be permeable (sand and gravel). However, if the near surface is effectively impermeable (clay) then a borehole soakaway would be required.
We regularly undertake soakaway testing on behalf of our Clients to accurately determine the permeability of the ground and therefore allow the viability of soakaways to be assessed. We tailor our approach to the site conditions and the Client’s budget.
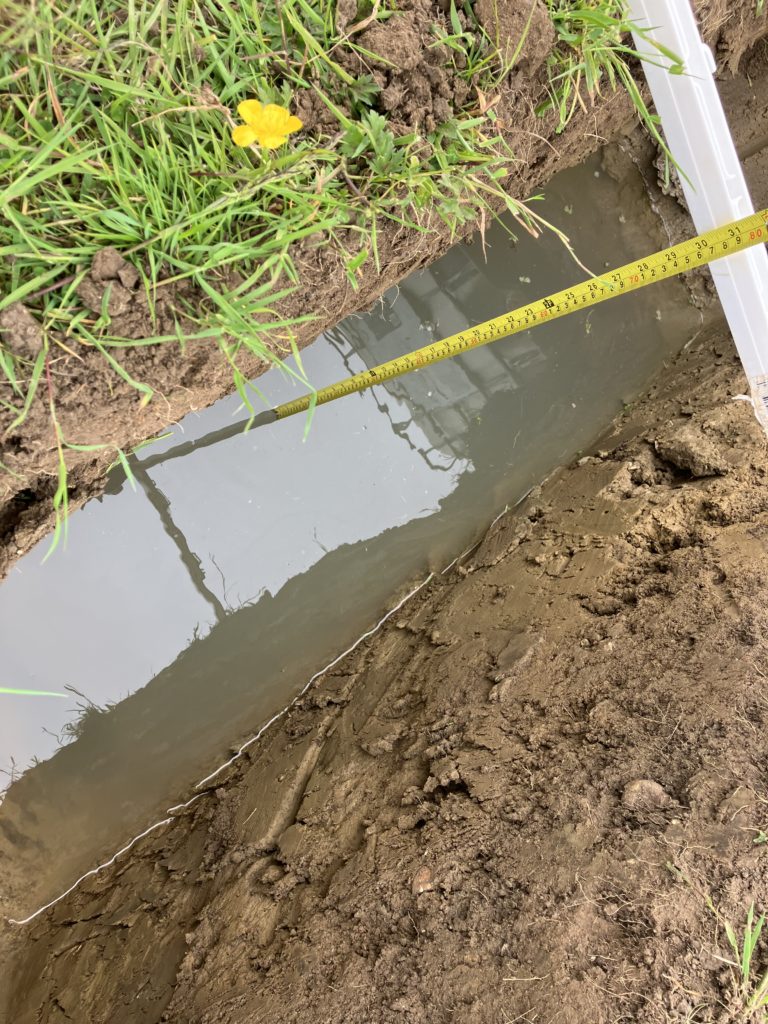
Shallow soakaway – BRE Digest 365
This method involves excavating a pit and then filling the hole with water. The time taken for the water level to fall from 75% to 25% is used to determine the permeability of the ground and thereby enable the soakaway to be designed.
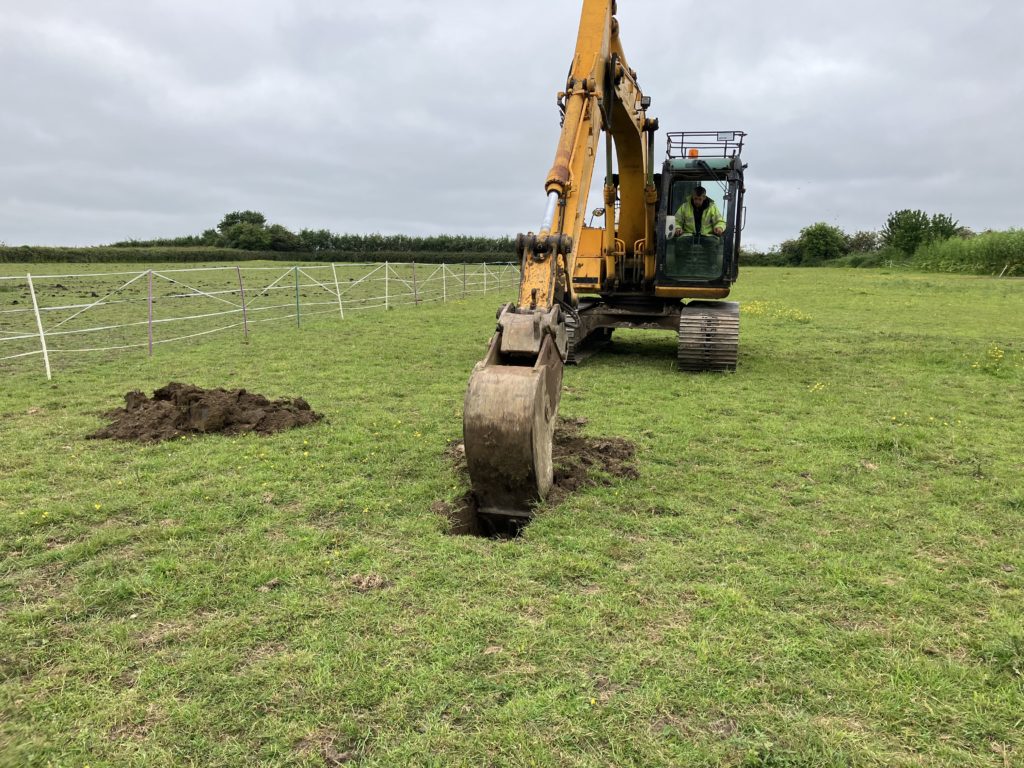
In order to be fully compliant with BRE 365 we use a JCB excavator to ensure the pit is of sufficient size. However, we also undertake tests in smaller, hand excavated pits (0.30m x 0.30m in plan) where a full size trial pit is not feasible. These tests still follow the principles of BRE Digest 365.
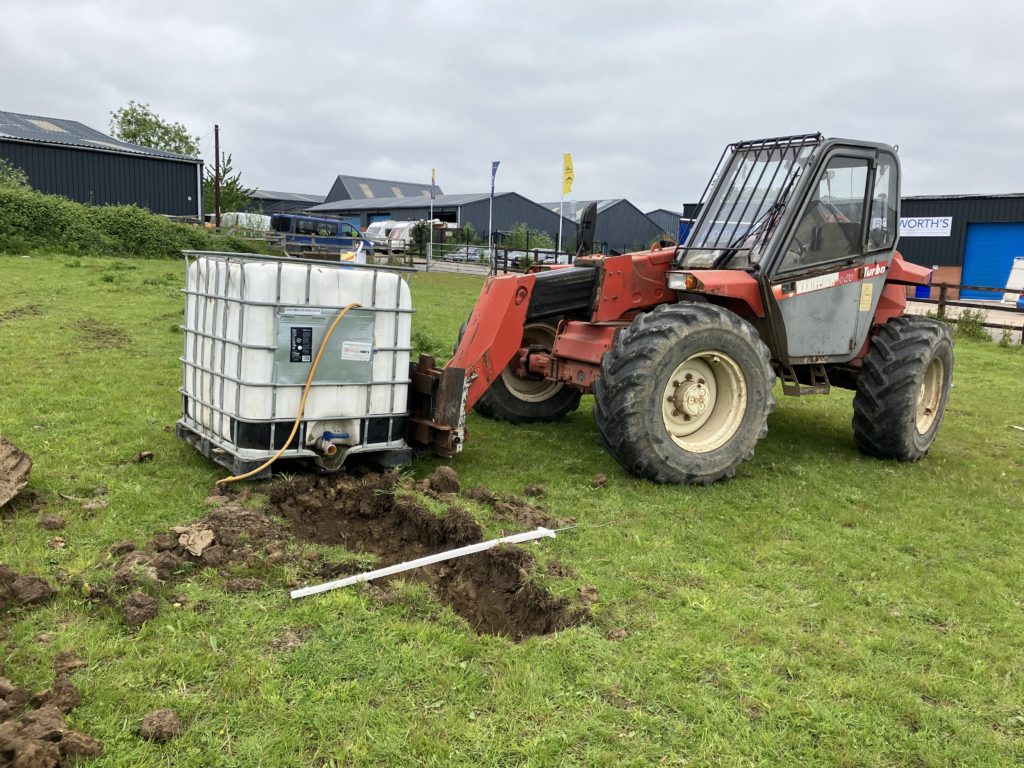



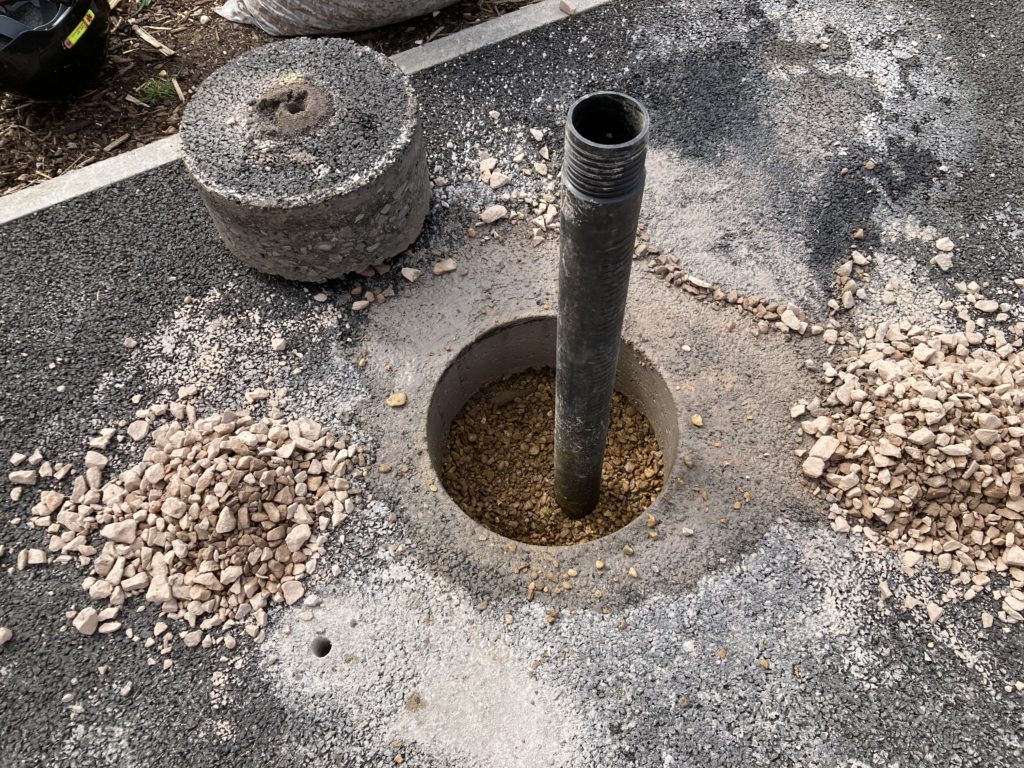
Variable head permeability
The method involves first drilling a borehole to the required depth so it’s sensible to do this at the same time as the ground investigation to save time and money. Water is then added (falling head) or pumped from the hole (rising head test). The water level is recorded at regular time intervals until the water has returned to the original level. The tests and subsequent interpretation are undertaken in accordance with BS EN ISO 22282.

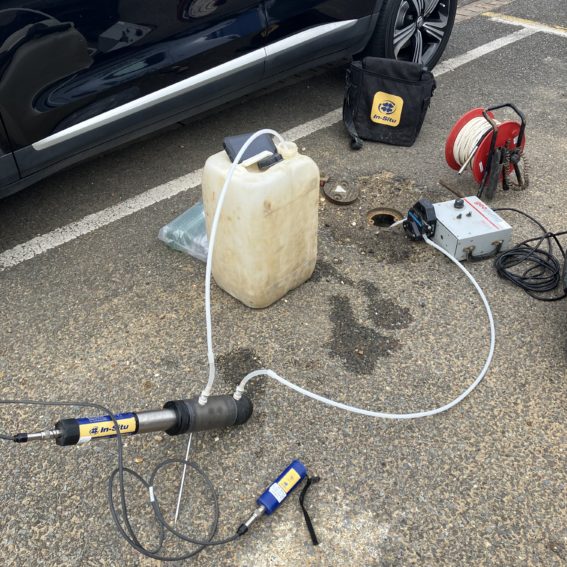
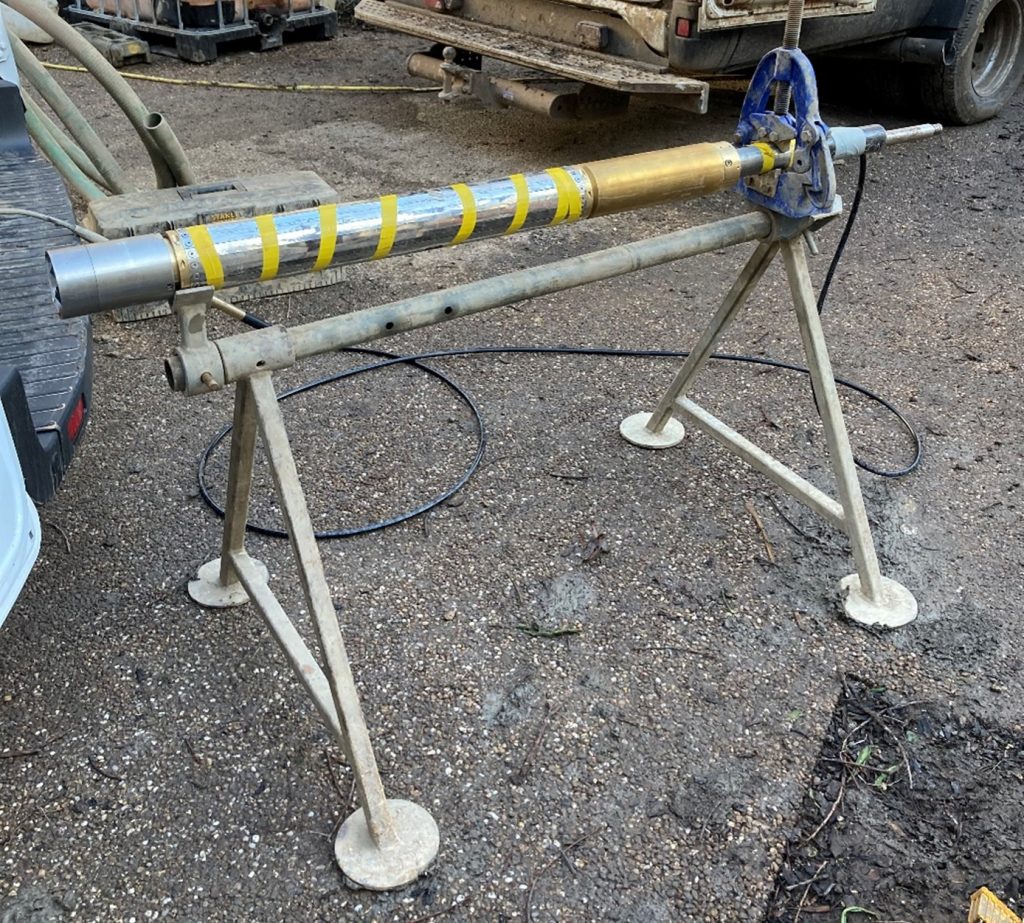
Pressuremeter testing
Pressuremeter testing is an advanced test to determine the in situ stiffness of the soil at various strains amongst other properties. The probe is inserted into a pre-drilled hole and then expanded radially. The rate of expansion and resistance to it is carefully monitored and analysed to derive geotechnical parameters.
We work closely with our specialist sub-contractor Cambridge In Situ to ensure the proposed tests will meet the objectives.

What Our Clients Say
"Vision Survey have worked with Soiltechnics for several years, initially forging a strong working relationship with their Manchester office, which has since expanded to include our respective southern offices. We appreciate their excellent professional conduct, their collaborative working approach and ultimately, in knowing that we can rely on them to meet our requirements."
Nathan Pickering, Regional Operations Lead – Vision Survey
"Having worked with Soiltechnics for almost ten years, they are considered a trusted member of our supply chain. Soiltechnics completed a robust selection process which highlighted their ability to perform with the utmost professionalism in regards to customer service, value for money and site safety. It is trusted consultants like Soiltechnics who we can depend on in our pursuit to provide the perfect product for our customers.”
Gavin Williams, Senior Pre Construction Surveyor – Willmott Dixon Construction Ltd
“Just wanted to say that I was very impressed with the site team this week. The site engineer showed great leadership on site, delivering the works on time, and kept us updated with daily diaries and updates throughout. The engineer also promptly provided me with certifications for all of the drilling rigs and equipment the guys were using without me having to ask for it, which isn’t typical of all of our subcontractors!”
Lewis Brown, Site Manager Projects – The Clancy Group



